 |
Written by Liz McDermott |

The toxicity hazard symbol, also known as the skull and crossbones pictogram, is a recognizable icon representing the danger of hazardous substances that can cause acute toxicity. It is a warning sign reminding us that not everything we encounter is safe, and we must take the necessary precautions to protect ourselves.
This toxic hazard symbol is critical in helping workers identify hazardous materials that can cause acute toxicity in the workplace. It is essential to OSHA's Hazard Communication Standard and WHMIS training. These workplace safety programs help prevent accidents and illnesses caused by exposure to toxic substances.
What does the toxic symbol look like?
The toxicity hazard symbol is a black skull and crossbones pictogram on a yellow background for countries outside the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals. Countries like the United States and Canada, which follow GHS compliance, require hazard pictograms to have a black symbol on a white background with a red border.
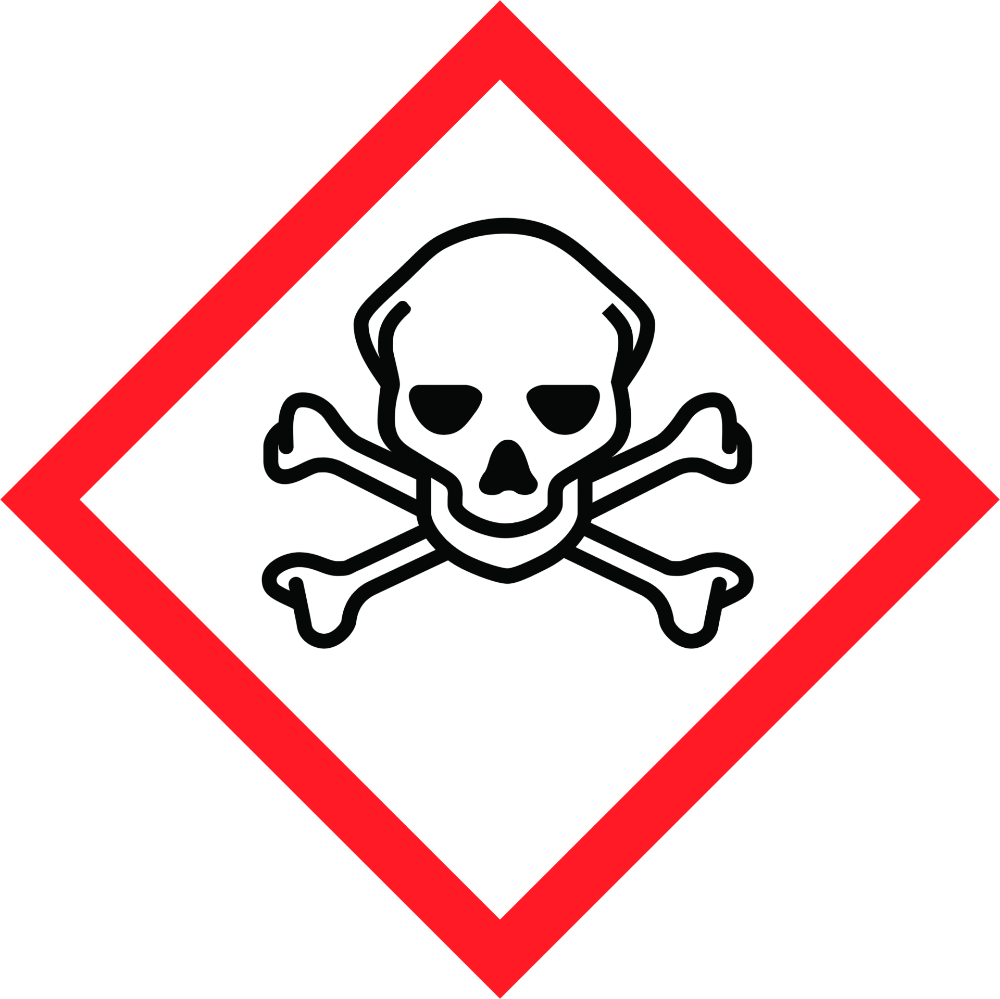

The skull and crossbones pictogram is recognized worldwide. It is commonly found on safety data sheets or labels of products that contain a hazardous substance that can cause acute toxicity.
What does the toxic hazard symbol mean?
The skull and crossbones symbol is used in a chemical label and safety data sheet to indicate the presence of a toxic substance or material that poses the risk of acute toxicity. This symbol is used to warn people about the health hazards and dangers of the hazardous substance so that they can take special precautions when handling the material.
It indicates that the material may be toxic if inhaled, ingested, or absorbed through the skin. Acute toxicity means that if you make contact with the hazardous material, a single dose can be life-threatening or poisonous.
Exclamation Mark Symbol
The exclamation mark symbol is often included with the skull and crossbones symbol since it communicates hazards such as skin or eye irritation, respiratory and skin reactions, and acute toxicity that can lead to organ damage or even death from brief exposure.
Which hazard classes use the skull and crossbones pictogram?
The skull and crossbones pictogram indicates the presence of acute toxicity in a hazardous material. Acute toxicity is the ability of a material to cause harm or injury to a person through a single or short-term exposure.
Toxic and Corrosive Substances
The symbol is used in hazard class 6 (toxic substances) and hazard class 8 (corrosive substances) under GHS. These hazard classes indicate the presence of poisonous substances that can potentially cause acute toxicity with life-threatening effects.
Industries and Chemicals
The toxic substance hazard class and corrosive substance hazard class are hazard classes commonly found in industries such as chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. These industries deal with hazardous materials, such as Ammonia and Hydrogen Sulfide, that can cause acute toxicity to workers if not handled correctly.
Using the skull and crossbones pictogram in these industries is critical for workers to recognize the potential hazards and take appropriate precautions to protect themselves from acute toxicity.

What signal words and hazard statements are used?
The signal word used with the skull and crossbones pictogram is "Danger." The term "Danger" indicates that the hazardous substance is severe and can cause significant harm or injury to a person, such as acute toxicity. The word is combined with hazard statements describing the specific hazards associated with the toxic substance.
The hazard statements used with the skull and crossbones pictogram describe the hazards associated with acute toxicity.
For example, the hazard statement "Fatal if swallowed" indicates that the substance can cause death if ingested. The hazard statement "Toxic if inhaled" suggests that the chemical can cause harm if inhaled.
The combination of the signal word and hazard statement provides essential information to workers about the health and physical hazards associated with acute toxicity. Workers can use this information to take appropriate precautions when handling the material to prevent accidents and injuries related to physical hazards that lead to target organ toxicity.
What is acute toxicity?
Acute toxicity is the ability of a material to cause harm or injury to a person through a single or short-term exposure. The route of exposure, the dose, and the duration of exposure determine acute toxicity. The three main routes of exposure are inhalation, ingestion, and absorption through the skin.
Acute Toxicity Symptoms
The symptoms of acute toxicity depend on the substance and the dose. Symptoms target organ toxicity can vary from mild to severe, including headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, seizures, and even death. The severity of the symptoms is directly related to the dose of the toxic substance.
Acute toxicity is a significant concern in industries that deal with hazardous materials. Workers must be trained to recognize the potential hazards of the materials they handle and use the appropriate safety products to protect themselves from harm.
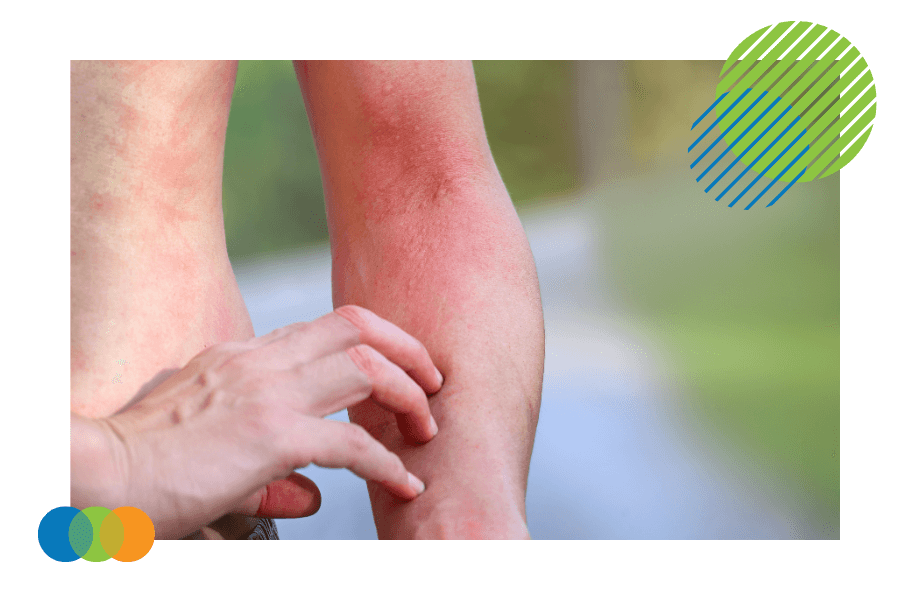
What are the hazards of products that have the skull and crossbones pictogram?
Products that have the skull and crossbones pictogram are hazardous because they can cause acute toxicity to a person if not handled correctly. The hazards associated with these products depend on the specific substance and the route of exposure. The three main routes of acute toxicity exposure are inhalation, ingestion, and absorption through the skin.
Inhalation of Toxic Substances
Inhalation from not keeping a container tightly closed, for example, can cause respiratory problems, including difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing. Keeping a container tightly closed can prevent exposure to these hazards.
Ingestion of Toxic Substances
Ingestion can cause stomach and intestinal problems, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Workers must be trained to take appropriate steps to protect themselves from these hazards by using safety products that prevent exposure.
Absorption Through Skin
Skin contact can cause skin irritation, rash, and chemical burns. The hazards associated with skin contact can cause severe skin corrosion. These health hazards can easily be avoided using appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves, to prevent skin contact and keep containers tightly closed.
Need help training workers on toxic exposure hazards?
Consider Vubiz online training courses:
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Personal Protective Equipment: The Basics (CCOHS)
- Handling Hazardous Waste
- Hazard Communication (OSHA)
- Hazardous Materials Transportation: 49 CFR Overview
- Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System (WHMIS)
What should I do in case of an emergency?
In an emergency involving a hazardous substance, it is essential to follow the appropriate procedures to ensure your safety and the safety of others. The first step is to evacuate the area immediately and call for help. If necessary, contact emergency services, such as the fire department or hazardous materials response team.
If you are exposed to a toxic substance, seek medical attention immediately. The symptoms of acute toxicity can vary, and it is important to receive prompt medical care to prevent further harm or injury.
After an emergency involving a hazardous substance, following the appropriate cleaning and disposal procedures is crucial. Contact the relevant authorities for guidance on properly disposing of the dangerous material.
Conclusion: Recognizing the Toxicity Hazard Symbol Can Save Lives
The toxicity hazards symbol is a critical tool that ensures workers know the hazardous materials they may be handling. It is an essential component of any workplace safety program, as it helps prevent accidents and illnesses caused by exposure to toxic substances. The skull and crossbones pictogram indicates acute toxicity in a material and is used in hazard classes 6 and 8 under the GHS.
Workers must be trained to recognize the potential hazards of the materials they handle and to take appropriate precautions to protect themselves from acute toxicity, like keeping containers tightly closed. Products that have the skull and crossbones pictogram are hazardous. In an emergency, it is essential to follow the appropriate procedures to ensure your safety and the safety of others.
Recognizing the crossbones pictogram can save lives. By understanding the potential hazards of toxic substances and taking appropriate precautions, workers can prevent accidents and injuries in the workplace. The symbol reminds us that not everything we encounter is safe, and we are responsible for protecting ourselves and others from harm.
For more information, please contact us to inquire about our safety training programs.
